Object-oriented programming (OOP) in Java organizes code around objects and classes, making applications more modular, reusable, and easier to maintain. When someone asks “what are the oops concepts in java”, they generally refer to four main pillars: encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction.
Overview of OOP in Java
OOP treats a program as a collection of objects that interact with each other, rather than a list of procedures. These objects are created from classes, which act as blueprints defining properties (fields) and behaviors (methods). Understanding these basics is essential before diving into oops concepts in java with examples or preparing for oops concepts in java interview questions.
In Java, everything revolves around classes and objects: a class defines the template, while an object is a specific instance of that template. A solid grasp of what are the oops concepts in java helps developers design systems that are flexible and easy to extend.
Encapsulation
Encapsulation is about bundling data (fields) and methods (functions) that operate on that data into a single unit, typically a class, and restricting direct access to the internal state. In practice, Java developers use private fields with public getters and setters to control how data is read or modified.
For example, imagine a BankAccount class with private balance and public deposit/withdraw methods; other classes cannot change balance directly but must go through controlled methods. Such patterns are commonly asked in oops concepts in java interview questions, especially around data hiding and access modifiers.
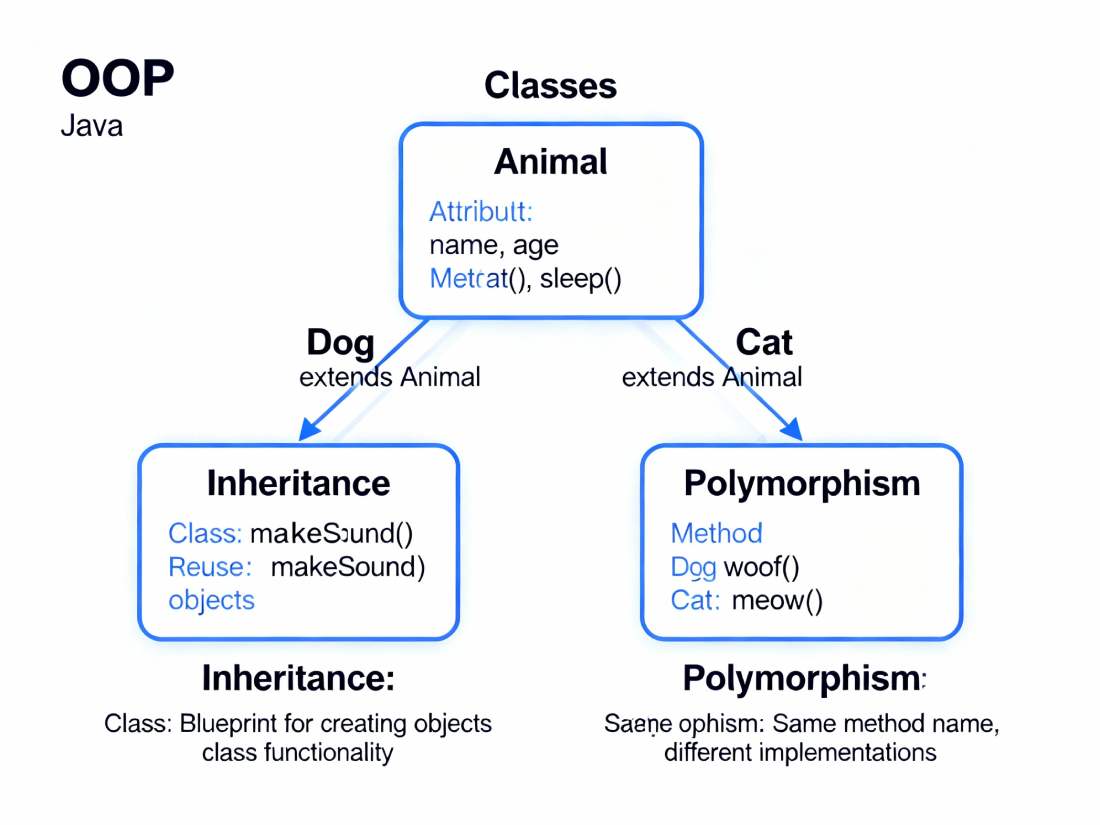
Inheritance
Inheritance allows one class (child or subclass) to reuse the properties and behaviors of another class (parent or superclass). In Java, this is implemented using the extends keyword, enabling “is-a” relationships like Dog extends Animal.
This mechanism avoids code duplication and is central when discussing oops concepts in java with examples, such as base Vehicle class and derived Car or Bike classes. Interviewers frequently include “what are the oops concepts in java” followed by deeper questions on types of inheritance and when to use it.
Polymorphism
Polymorphism means “many forms” and lets the same method name behave differently depending on the context. Java supports compile-time polymorphism via method overloading and runtime polymorphism via method overriding.
For instance, a print() method might accept different parameter types (overloading), while a subclass overrides a parent method to provide specialized behavior. These patterns are classic topics in oops concepts in java with examples and regularly appear in oops concepts in java interview questions focusing on dynamic dispatch and method binding.
Abstraction
Abstraction focuses on exposing only essential features while hiding internal implementation details. In Java, abstraction is mainly achieved using abstract classes and interfaces that define what an object can do, not how it does it.
For example, a Payment interface may declare pay() and refund() methods, while classes like CreditCardPayment or UpiPayment provide specific implementations. When candidates answer “what are the oops concepts in java”, they are expected to describe abstraction alongside real-world design scenarios.
Classes and Objects
Beyond the four pillars, many explanations of oops concepts in java with examples start with classes and objects as foundational concepts. A class defines attributes and methods, while objects are concrete instances created using constructors.
Real-world analogies, like a Car class and objects such as myCar or yourCar, help clarify how state and behavior are encapsulated within each instance. This understanding underpins most oops concepts in java interview questions that test how well you can map business requirements to classes and objects.
Why OOP Matters in Java
OOP in Java reduces complexity by breaking large systems into smaller, interacting objects. It improves reusability through inheritance, maintainability via encapsulation, and flexibility using polymorphism and abstraction.
When preparing for interviews, revising what are the oops concepts in java along with small code snippets and use cases will help answer oops concepts in java with examples and oops concepts in java interview questions confidently.